When you need to transfer money overseas, you walk into a bank, and your money is transferred to any part of the globe.
How does it happen? The answer is Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunications (SWIFT), a member-owned corporation that provides safe and secure transactions between financial institutes.
Since 1973, SWIFT has dominated financial transactions across the globe. It was founded with 239 banks in 15 countries. By 1977, it grew to 518 institutions in 22 countries. SWIFT recorded an average of 41.6 million FIN (financial information) messages per day in 2021. As compared to the previous year, traffic grew by 11.8%.
How Does SWIFT Function?
SWIFT assigns a unique 8 to 11 – character code to each financial institute. The code is called the bank identifier code (BIC), SWIFT ID, or SWIFT code. Let’s assume a Bank of America (BAC) customer wants to transfer money to the Bank of Italy. The customer can walk into the bank with their friend’s account number and SWIFT code to process the transaction.
Bank of America (BAC) will transfer the payment across the secure SWIFT network & once the Bank of Italy receives the payment, it will credit the amount to the friend’s account.
Drawbacks of SWIFT
Over time, financial institutes realised that SWIFT’s 40-year-old MT messaging standard covering payments, trade services, securities, and trading was longer suitable. It had limited data-carrying capabilities and was extremely expensive to maintain. The following reasons highlight the major drawbacks of using SWIFT :
- Most SWIFT clients have huge transactional volumes for which manual entry of instructions is not feasible.
- While SWIFT paid acceleration consumes comparatively shorter time, the standard SWIFT transfers are time-consuming, the payment realisation taking even two days after it was sent.
- SWIFT transfers are incomparably high priced and often defined as a percentage of the transferred amount. The minimum and maximum values are set differently for each country.
- The need for SWIFT automation is growing; however, it comes with increased cost.
- A disparate set of standards causes integration issues within financial institutes.
Why Was ISO 20022 Introduced?
There was a need to develop a framework for standard messages across various domains such as retail payments, trade, securities, foreign exchange (FX), etc. This led to the emergence of ISO 20022 in 2004, a global standard for electronic exchange between financial institutes.
ISO 20022 creates a common language and model for exchange across the globe. Banks worldwide are preparing themselves to transition from SWIFT international messaging to a new, highly structured, and information-rich standard ISO 20022.
Standards are critical components while initiating and reporting financial transactions. An international standard simplifies interoperability and enables the efficient, consistent, and secure exchange of files.
Large financial institutes tended to develop, approve, and implement standards without seeking inputs from other well-known organizations. The resulting inconsistency led to multiple issues and hindered interoperability.
A four-year window is provided for the global SWIFT migration. It is estimated that by 2025, the standard will support 80% of transaction volume and 87% of transaction value globally. ISO 20022 provides high-quality metadata consisting of descriptions of messages, business processes, and maintenance processes, enabling assured payments at reasonable rates for all the involved institutes.
What is ISO 20022?
ISO 20022 is an open, international standard introduced to develop financial message standards for today’s real-time payments world. It ushers in a global, common language of financial communications.
Importantly, everybody in the industry can participate and implement the standard since it’s not being controlled by any individual organization. The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) first introduced it to give the financial industry a platform for developing messages in extensible markup language (XML).
ISO 20022 improves communication, makes sense of different meanings, and gets everyone on the same page. These goals are accomplished by a syntax-independent approach (simplified structure and form of a message) and semantics (the meaning of these messages).
How Does ISO 20022 Work
ISO 20022 uses three main ingredients to create a standardized communication recipe across borders and industries.
- Business process and concepts – ISO 20022 methodology begins with defining the roles, actors, and the information involved. The data is then organized into components called business elements.
- Logical message independent of syntax – Describes the information needed to perform a specific business activity, independent of syntax.
- The syntax – Relates to the physical representation of the logical message. XML is specified as the primary syntax.
What ISO 20022 helps Define & Compliance to it Helps Achieve/Assure?
One of the major advantages of ISO 20022 is that it captures business transactions in a syntax-independent manner.
ISO 20022 has a centralised ‘Dictionary’ of business terminologies across all financial messages and institutes. It also offers a ‘Business Process Catalogue’.
Data Dictionary
The data dictionary contains business concepts, message concepts, and data types. The advantage is that anyone who wants to create a compliant message has the liberty to name the elements. But they need to link to base types mentioned in the repository. This ensures common understanding among all the parties.
Business Process Catalogue
The catalogue contains business areas that are described in detail using business processes using message flow diagrams. Each message is described in a message definition, which is converted into ISO 20022 syntax message schema.
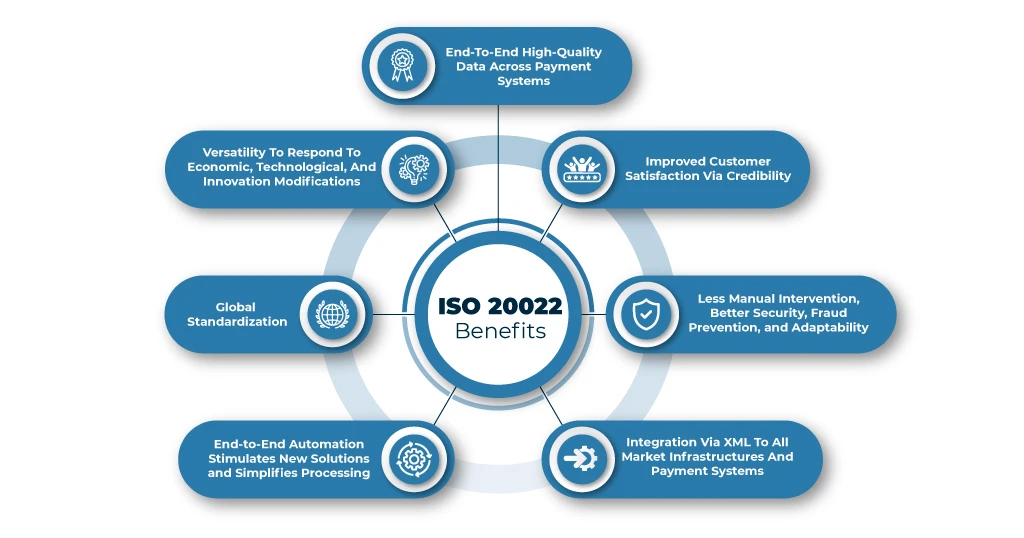
What are the Benefits of ISO 20022?
Global adoption of ISO 20022 will create a common language and provide high-quality data transfer and faster payments for everyone involved in the payment chain. The open standard is flexible to changing needs and requirements of the payment industry. Some of the key benefits of ISO 20022 :
- High-quality, better-quality data end-to-end across payment systems.
- Increased transparency leads to higher customer satisfaction.
- Less manual intervention, resulting in accurate compliance, higher security, fraud prevention, and better resilience.
- Efficient integration using advanced XML technology that reaches every market infrastructure and payment system.
- End-to-end automation encourages the creation of new services and straight-through processing.
- Worldwide adoption of the standard.
- Increased flexibility, making it more responsive to changes in the economy, emerging technologies, and product innovation.
Preparing for ISO 20022 Migration
Several Fortune Global 500 companies have collaborated with World banks to enable ISO 20022 migration. Financial systems, financial institutes, and players are now working to become ISO 20022 compliant.
Failure to comply in the four-year migration window can lead to shutting down of international payments for financial institutes. There were several roadblocks on the way. Firstly, they must integrate all the points with multiple systems which have payment systems across the globe.
Financial institutes also need to ensure that the bank is compliant with SEPA credit transfer (SCT). A wide range of local product variants and processes must also be incorporated.
Global Impact and Adoption on ISO 20022
Globally financial institutes will migrate from SWIFT MT financial messaging system to highly structured, meaningful, and data-rich ISO 20222 standards. ISO 20022 will dominate high-value payments by 2023, accounting for 79 percent by volume and 87 percent by value globally.
Over 70 countries have already adopted ISO 20022, including Switzerland, China, India, Japan, Singapore, etc. ISO 20022 will apply to the domestic, automated clearing house (ACH), real-time, high-value, and cross-border payments.
Japan’s Central Bank redesigned its real-time inter-banking system to ensure it is ISO 20022 compliant. Singapore’s Central Bank has started the transition and will migrate this year. Systems in China and India are already compliant and reap the benefits of ISO 20022.
How to Stay Compliant with ISO 20022?
- Kickstart the transition process and access payment infrastructure.
- The standard involves processing large volumes of data and at high speed for real-time payments, daily liquidity management, etc.
- Allow adequate time for implementation.
- Transparent communications between all stakeholders, including the financial. institutions, business clients, customers, implementation partners, and importantly, the transition agents within the corporation.
Major Challenges of ISO 20022 Implementation
- Legacy standards, processes, and workflows used before ISO 20022 must be reviewed, mapped, and translated to new standards. Outdated legacy technologies need to be updated, replaced, or converted. This involves a budget agreed upon by all the stakeholders, institutes, and partners.
- There are different specifications for different payment schemes, e.g. : HVPS+ and CBPR+.
- ISO messages are much folded longer than standard payment messages; this means better infrastructure is required to manage additional ISO 20022 information.
ELAIT’s Services For Migration to ISO 20022
- Establish policies, practices, and standards for data management based on ISO 20022.
- Measure, correct and monitor data quality that focuses on business value and correcting data at optimal locations.
- Ensure data consistency and accuracy, define data formats, ensure regulatory adherence to building robust organizations.
- Manage operational risks to control operating costs.
Elait specialises in Ab Initio implementations and helps corporations adopt this powerful platform for their Data Engineering initiatives.
Ab Initio can be used in meeting ISO 20022 messaging standards and tracking flows throughout the process. As a transformation tool, it can create the format for any file and break it down into more granular details to help trace the sources and targets of the transfer details.
This helps banks reassure their payment ecosystem for every transaction and empowers financial firms to make better decisions, find new opportunities, stay regulatory compliant and safeguard business operations.
Reference
https://www.iso20022.org/financial-repository
https://www.swift.com/standards/iso-20022/iso-20022-programme
https://www.ir.com/guides/what-is-iso-20022
.